Time:2025-06-07 Views:1

CNC electronic equipment, which includes controllers, servo drives, and other sensitive electronic components, is highly vulnerable to electromagnetic interference (EMI). Electromagnetic shielding protection is essential to ensure the reliable operation of these systems, as EMI can disrupt the normal functioning of the electronics, leading to errors in machining, reduced accuracy, and even system failures.
The basic principle of electromagnetic shielding is to block or redirect electromagnetic waves using conductive or magnetic materials. For CNC electronic equipment, various shielding techniques are employed. One common method is to enclose the sensitive components in a metallic enclosure, often made of materials such as aluminum or steel. These metallic enclosures act as a Faraday cage, preventing external electromagnetic waves from penetrating the interior and interfering with the electronics. The enclosure must be properly grounded to ensure that any induced electrical charges are safely dissipated.
In addition to the overall enclosure, individual components within the CNC electronic equipment may also be shielded. For example, printed circuit boards (PCBs) can be designed with shielding layers, such as copper foil or conductive coatings, to protect the delicate electronic circuits from EMI. Connectors and cables are also critical areas for electromagnetic shielding. Shielded cables, which have a conductive outer layer, are used to transmit signals between different components of the CNC system. The shielding layer of the cable is connected to the grounded enclosure at both ends to prevent electromagnetic waves from coupling into or out of the cable.
Another aspect of electromagnetic shielding for CNC electronic equipment is the use of electromagnetic - absorbing materials. These materials, such as ferrite beads or electromagnetic - absorbing gaskets, can be placed in strategic locations to absorb and dissipate electromagnetic energy. Ferrite beads, for instance, can be inserted in series with power or signal lines to suppress high - frequency noise.
Furthermore, proper layout and grounding design within the CNC electronic equipment are crucial for effective electromagnetic shielding. Components should be arranged in a way that minimizes the length of signal traces and reduces the formation of electromagnetic loops. A well - designed grounding system helps to ensure that all components are at the same electrical potential, reducing the risk of electrical noise and interference. By implementing comprehensive electromagnetic shielding protection measures, CNC electronic equipment can operate reliably in environments with high levels of electromagnetic radiation, ensuring the precision and stability of CNC machining processes.
Read recommendations:
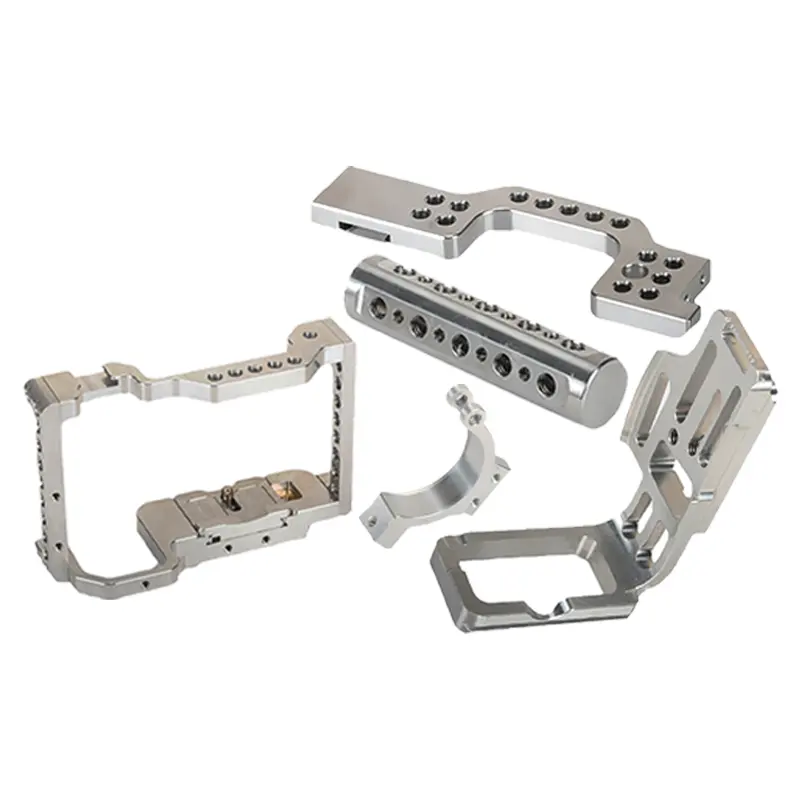
Camera Cage with 1/4" 3/8" Hole with Arri Location Holes for Sony Fx3 FX30 ILME-FX30 Cinema Camera
Upgrade Camera Cooling Fan for Sony/Canon/FUJIFILM/Nikon DSLR Cameras Video Shooting Accessories
Full Camera Cage for Canon EOS R8 /RP Camera Aluminum Alloy Film Movie Making Camera Video Cage Rig